M. Dastjerdi a, Z. Abassi Radmoghadam a,b, M. Valadbeigi a, A. Dastjerdi a, F. Nasiri a, S. Akbari a,b,c, A. Akbari c
aNanoSciTec GmbH, Hermann Weinhauser str. 67, Munich, 81867, Germany
b BioMedEx GmbH, weyringerg 37 Stiege 1, 1040, Wein, Austria
c GreenNanoTech Kft, Westend Business Center, 22-24 Váci street, Budapest, 1132, Hungary
Abstract
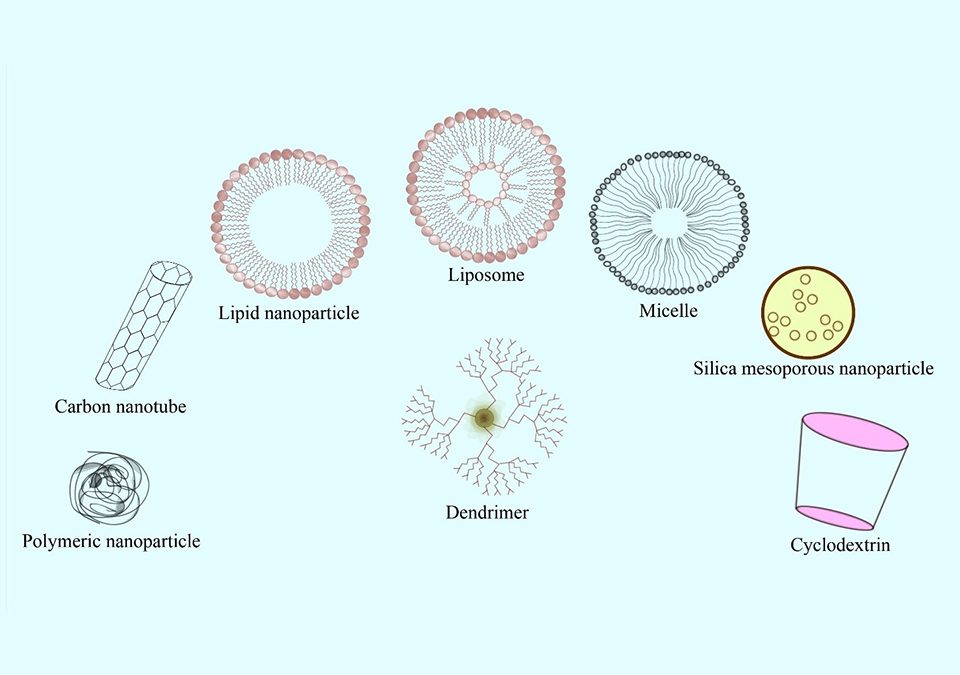
The past few decades have witnessed a significant amount of research on lung cancer therapy as one of the leading mortality cause globally. Conventional treatments have disadvantages such as limited water solubility, drug resistance, and the damaging of healthy cells, resulting in decreased efficacy. As this outlook reports, immunotherapy integrated with drug delivery systems has been applied to exploit the synergistic and targeted effects. On the other hand, nanomedicine for cancer therapy has boosted efficacy and mitigated the negative effects substantially. Despite the persistence of obstacles such as drug resistance and insufficiency of stability, clinical studies demonstrated notable improvements in the cytotoxic efficacy of medications and in lowering treatment-related adverse effects. Technical approaches incorporating nanoparticles and innovative delivery strategies to enhance the effectiveness of targeted immunotherapy have been established. In the present review, a summary of the most promising literature aimed to break new ground in the use of immunotherapy and lipid and micelle-based nano drug delivery systems for lung cancer therapy has been presented, along with describing their key benefits, drawbacks, and prospects. The future of lung cancer therapy based on immune modulation will probably be combined with improved drug delivery systems to generate treatment methods of high efficacy.
Keywords: Immunotherapy, Nanocarriers, Drug delivery, Lung cancer
© Article info: Accepted by: 11 October 2023, Published by: 24 October 2023.
Doi Number: https://doi.org/10.52319/j.nanoscitec.2023.25