Abstract
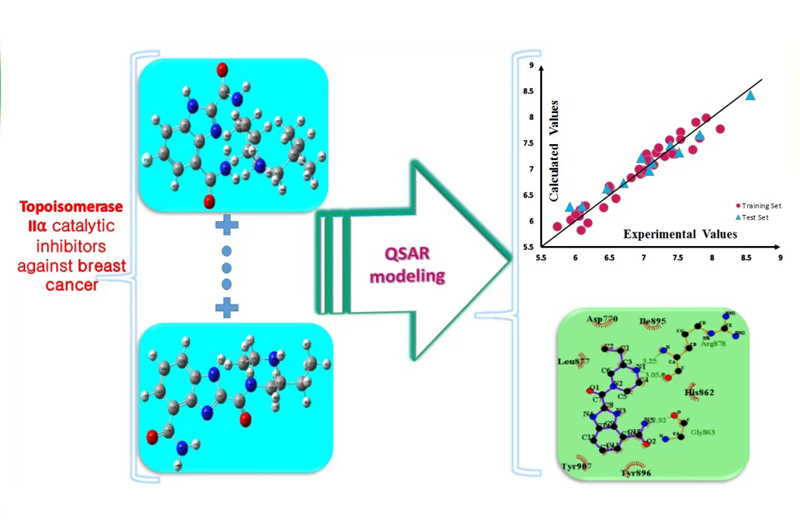
Structural analysis of topoisomerase IIα catalytic inhibitors exhibited anti-tumor properties to use them in cancer therapeutic procedures. In this study, a quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) modeling including multiple linear regression (MLR) and least squares-support vector machine (LS-SVM) analysis was applied on a series of 46 synthesized xanthone derivatives as topoisomerase IIα inhibitors. It was aimed to predict half-maximal inhibitory activity (IC50) of the compounds against breast cancer cell line HCT15 using the best computational method with the least error prediction. Genetic algorithm multiple linear regression (GA-MLR) explored the functional parameters of the final models. The achieved QSAR models presented a reliable relationship between chemical structure properties as descriptors and the inhibitory activities of compounds.
The models were confirmed using Leave one out-cross-validation (LOO-CV) method (for the best linear model including whole dataset R2 = 0.955, Q2 = 0.930, RMSE = 0.151, F = 115.593 and for the best non-linear model R2 = 0.981, Q2 = 0.971, RMSE = 0.099, F = 258.902). So, it was demonstrated that these models especially non-linear models are predictive models of high quality that can produce appropriate inhibitory activity prediction of the compounds to use them in pharmaceutical industries.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11224-020-01543-7